Occupational therapists and physical therapists should provide complementary therapy to patients with rheumatoid arthritis. They need to complement the therapy and education of others, so that patients are not confused and can manage the disease effectively and efficiently. If you want you can also get arthritis physiotherapy online through physio.family/arthritis-pain-relief.
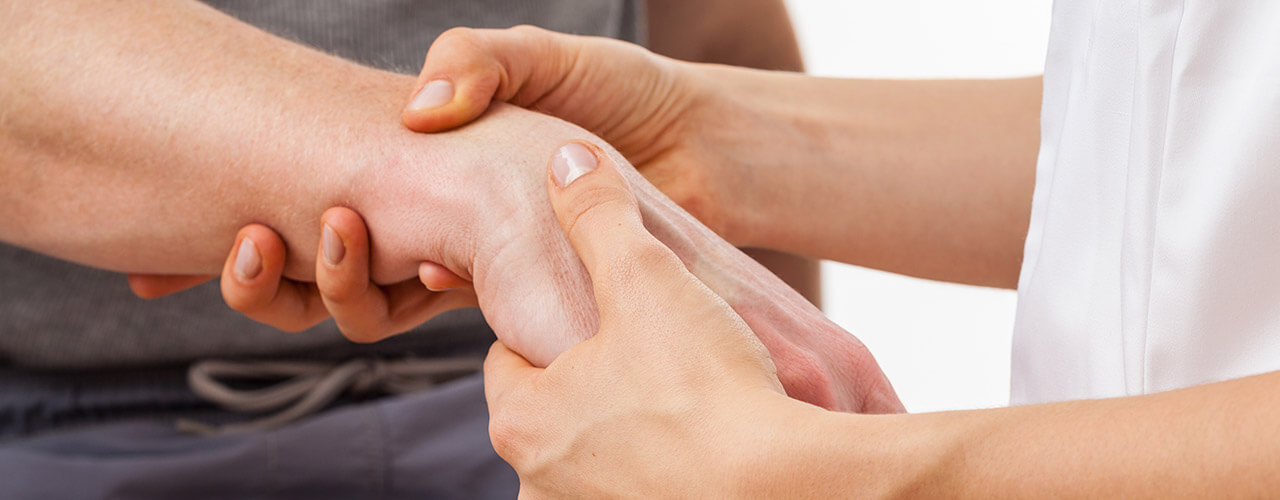
Image source:-Google
The greatest contribution that both the occupational therapist and the physical therapist make to the patient with this disease is with pain relief, improving mobility and functional capacity, as well as managing the mental and cognitive perspective in the face of pain and perceived deterioration.
Objectives of the physiotherapist and occupational therapist
1. Educate and assure the patient about the disease, its process, prognosis and what to expect
2. Educate, instruct and demonstrate energy conservation methods and their benefits
3. How to manage maintenance of joint range of motion through exercise, heat modality and protection
4. How to build strength and endurance through exercise, mental visualization and insight
5. Prevent or slow disease using approaches such as splinting, adaptive and protective approaches
6. How to maintain or improve mobility and function, allowing and encouraging the patient with the disease to participate as much as possible in activities of daily living and mobility. Mental approaches to stress management, motivation, and empowerment are frequently used to encourage and empower the rheumatoid arthritis patient to improve as much and as often as possible.
7. Provide support, counseling, and environmental modifications (social and physical) to facilitate the patient's cognitive and physical adjustment to the disease
8. Reintegrate the patient to his home, work and social life, with rheumatoid arthritis.

